Farmer's knowledge
Durian Tree – Characteristics, Cultivation Techniques, and Effective Pest & Disease Control
General Introduction to the Durian Tree
The durian tree (Durio zibethinus) is a tropical fruit tree with high economic value, known for its distinctive aroma. It is a long-lived perennial, commonly cultivated across Southeast Asia, especially in Vietnam’s Central Highlands and Southeastern regions.
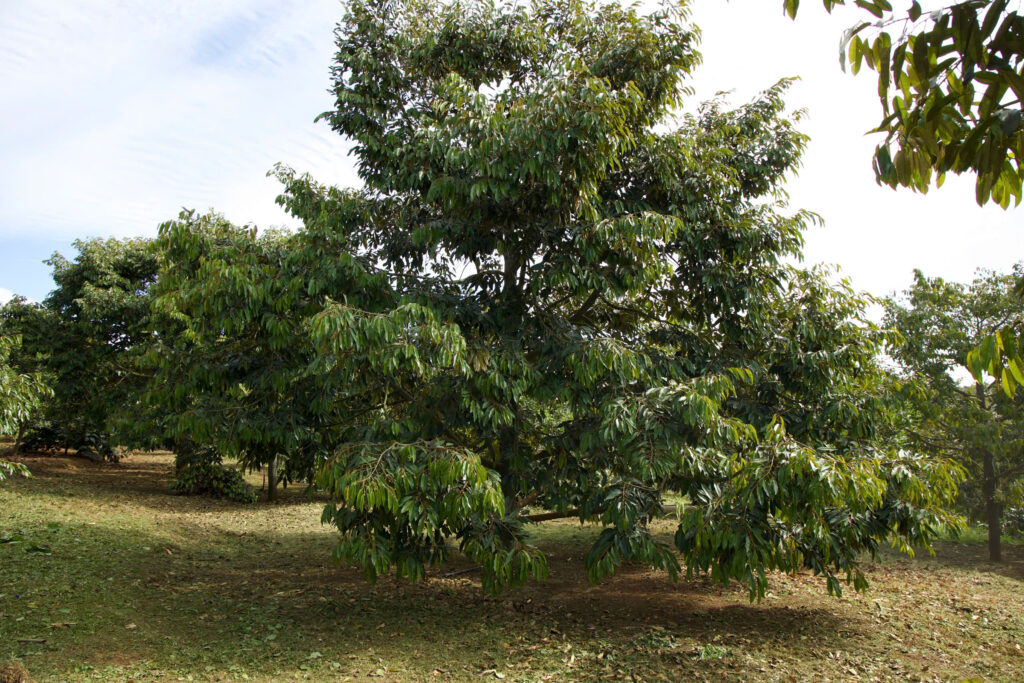

Figure 1: A durian orchard in the early morning, with fresh and peaceful atmosphere
Biological Characteristics of the Durian Tree
- Mature trees reach a height of 10–20 meters.
- The tree has a straight wooden trunk, with grayish-brown bark, which is vulnerable to fungal infections and pests.
- Leaves: are oval-shaped, alternately arranged, with a coppery underside.
- Durian flowers grow in clusters, bloom at night, and are primarily pollinated by bats.
- Durian fruit has a spiky shell and contains creamy yellow segments with a rich taste and strong aroma.
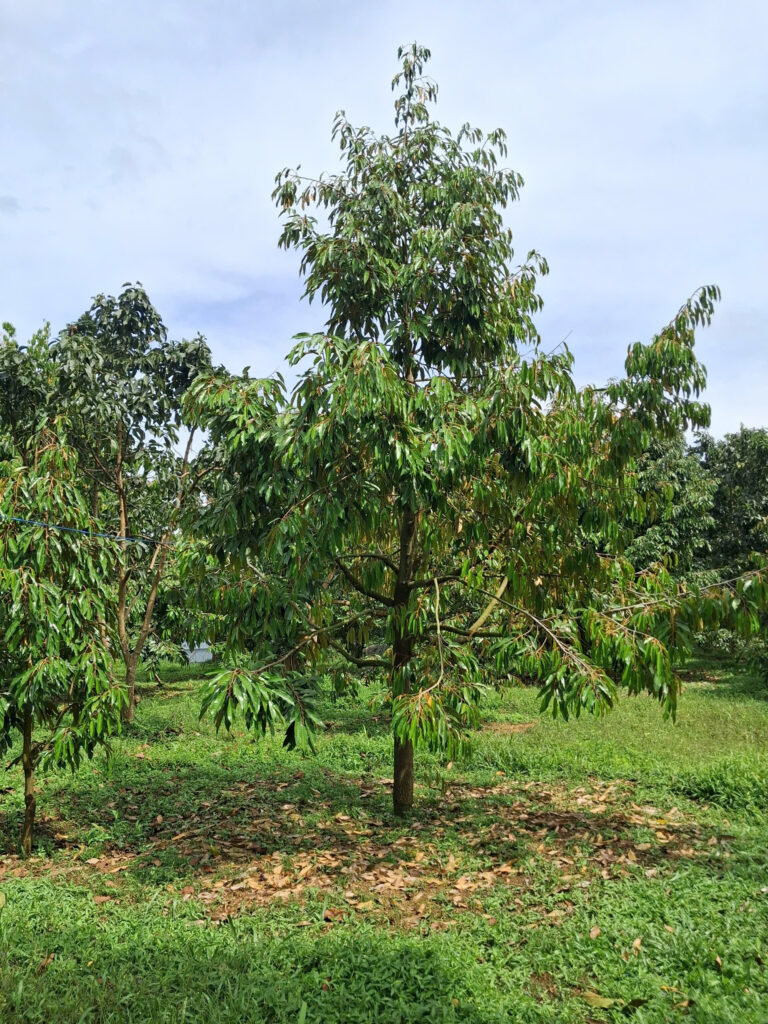

Figure 2: A healthy durian tree with a thick trunk and dense foliage
Common Durian Varieties in Vietnam
- Ri6 Durian – Rich sweet flavor, thick flesh, low fiber content.
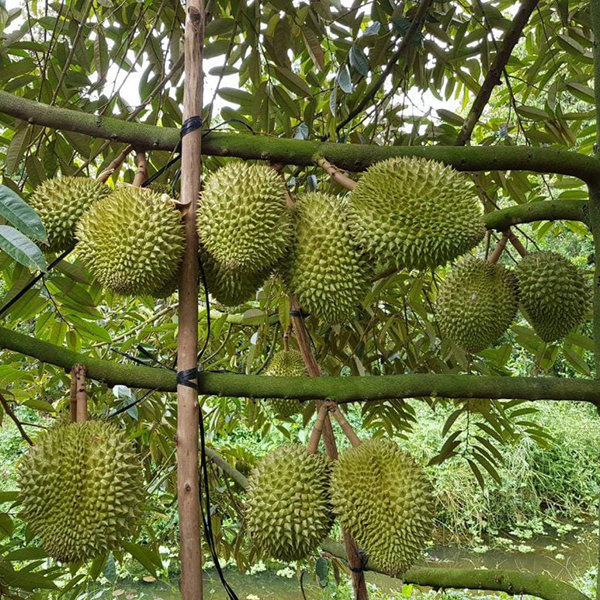

Figure: Variety Ri6
- Dona (Monthong) Durian – Large fruit, high yield, firm flesh.

Figure 4: Dona – Thai variety
- Musang King Durian – Imported from Malaysia, high commercial value.
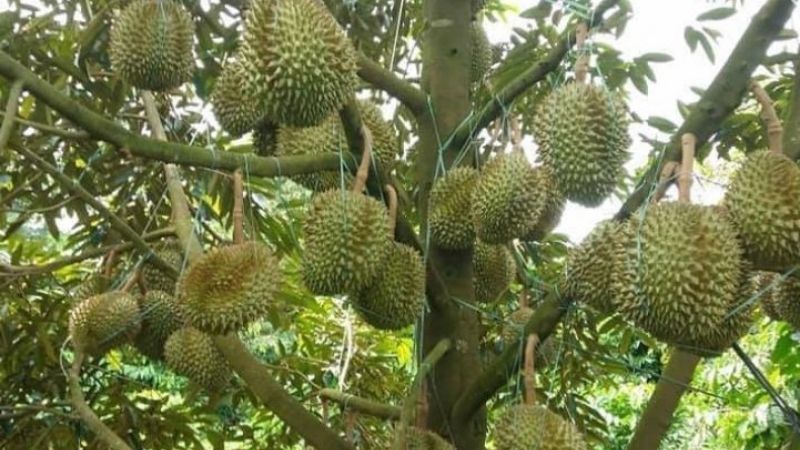

Figure 5: Musang King – Popular variety in Malaysia and Singapore
Effective Durian Cultivation Techniques
1. Land Selection and Garden Design
- Use loose, well-drained soil rich in organic matter (pH from 5.5 – 6.5).
- Dig planting holes 60x60x60 cm in size and apply well-decomposed manure mixed with lime as a base fertilizer.
2. Planting Season
- In Southern Vietnam: May to July (early rainy season)
- In Central Vietnam: August to October
3. Care and Maintenance
- Water properly, avoiding prolonged waterlogging.
- Prune branches to shape the canopy, allowing ventilation and reducing pest infestations.
- Apply fertilizers regularly: NPK, organic microbial fertilizers, and micronutrients.
Pest and Disease Control in Durian
1. Phytophthora Fungus Causing Root Rot and Stem Canker
- Symptoms:Oozing sap from the trunk, blackened bark, leaf wilting, and gradual tree death.
- Treatment Measure:
- Remove infected parts of the plant.
- Spray copper-based fungicides, Fosetyl-Al, or Metalaxyl at the affected areas.
- Enhance the garden’s drainage system to avoid prolonged moisture.
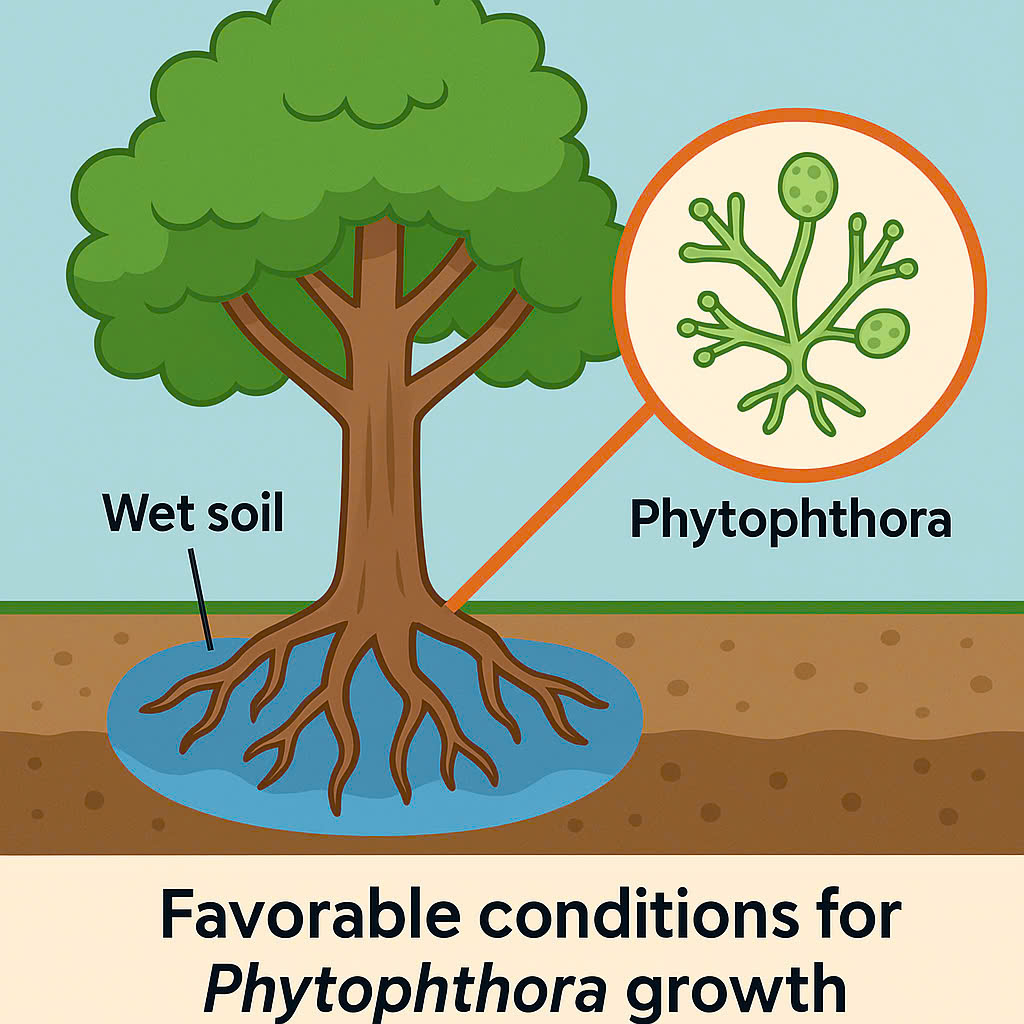
Figure 6: Infographic illustrating the tree structure and areas prone to Phytophthora fungus development
2. Stem Borers, Mealybugs, Red Spider Mites
- Use biological traps or spray plant protection products at the correct dosage.
- Prune branches and leaves, clean the base of durian trees, and interplant with insect-repelling crops.
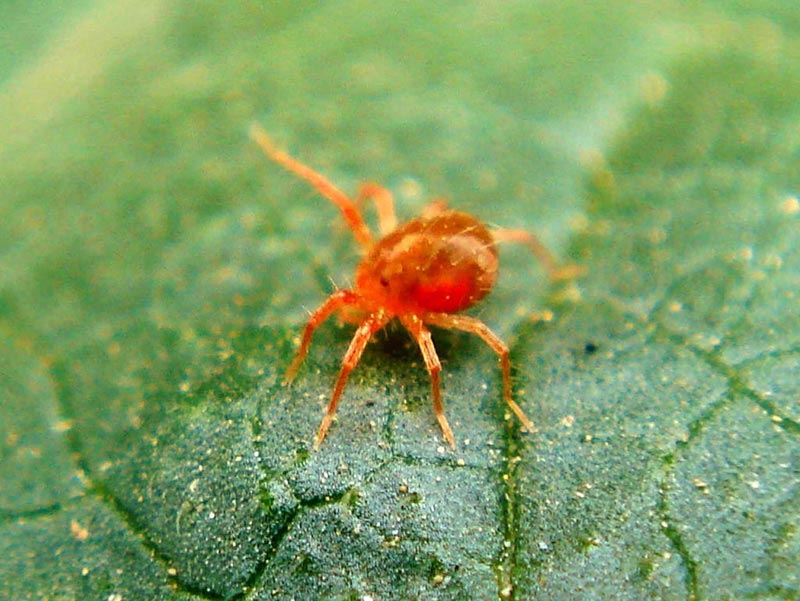

Figure 7: Image of red spider mites causing harm to crops
Drainage System and Sustainable Cultivation
To effectively prevent diseases in durian trees, designing drainage ditches and planting on raised beds is a sustainable solution. This promotes healthy root development and reduces fungal diseases.
Conclusion
In summary, according to the Department of Crop Production – Ministry of Agriculture of Vietnam, durian is a potential fruit tree in the transformation of crop structure in the South. In general, the durian species is a high-value cropwhen cultivated using proper techniques and effective pest and disease control.. Về việc lựa chọn giống tốt, canh tác bền vững và kiểm tra định kỳ sẽ giúp bà con nông dân đạt được năng suất cao, chất lượng quả ngon và ổn định thị trường đầu ra.
Interested in learning about dragon fruit cultivation techniques? Check it out here
